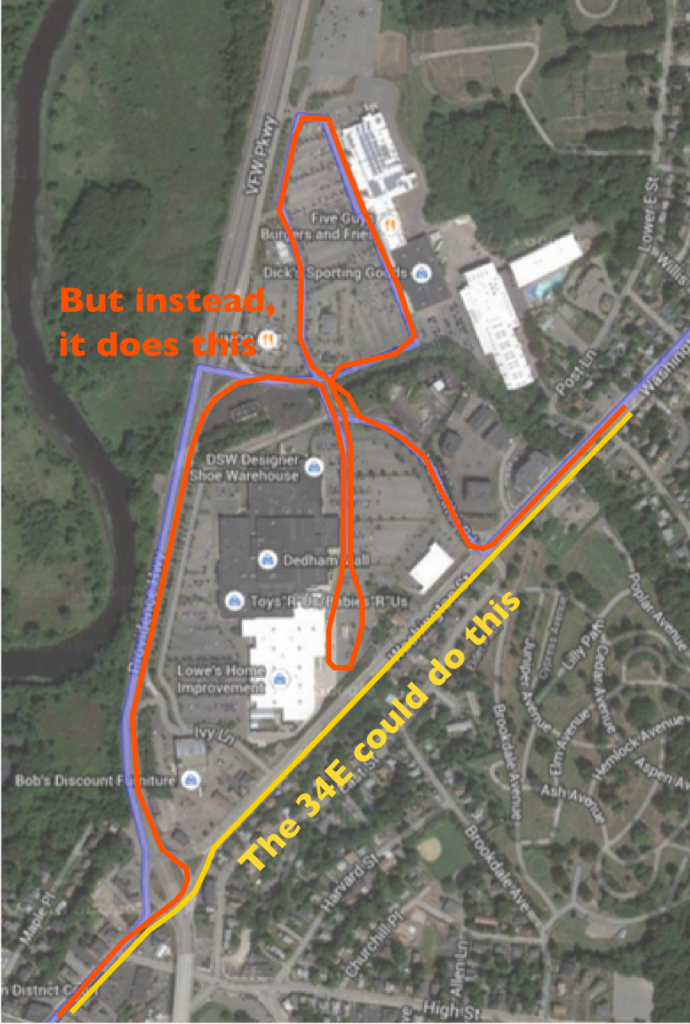
In this post I’ll describe something which is probably unfamiliar to big city transit system users, but which is very familiar for those who use smaller systems: a pulse. A pulse is a timed transfer between multiple routes in one location (or, in some cases, multiple locations) where buses wait for each other in order to allow passengers to transfer between them. Large systems with complex networks generally don’t use pulses both because of the complexity of scheduling and bus frequency: a transfer will often only mean a few minutes’ wait. But with 30- or 60-minute headways on many smaller systems, a pulse is an efficient means to create a usable network.
There are four requirements for a pulse system to be feasible:
- The system must be small enough. With more than 15 or 20 routes, the complexity of scheduling every bus to one central point will overwhelm the pulse savings, and may also result in inefficient and overlapping routings to reach the pulse location. Some large systems may have pulse features in peripheral locations, or certain times of day.
- A convergence of routes. Trying to schedule multiple pulse meets at multiple locations is quite complex, and mid-route meets are operationally inefficient since buses usually need a few minutes of schedule padding to allow for variances in travel times. Most pulses take place at a central location where multiple routes lay over. So a network needs to be focused on a single location.
- Minimal traffic. Pulse networks are based on buses keeping their schedules. In cities with heavy traffic, unless there are busways, a bus that is delayed for five or ten minutes may result in the rest of the pulse being delayed, or passengers missing transfers.
- Not too much crowding. Crowding on transit is generally a good thing, since it means that people are using the system. Too much crowding, in addition to passenger discomfort, leads to slower run times which, much like traffic can cause a pulse network to break down. In addition, crowding shows that more frequent buses are needed, and pulse networks provide coverage and predictability, but are not easy to scale, because to change the headways on one route, you need to change the headways on all the others.
- Routes have to be similar in length. Pulses work best when a single bus can make a roundtrip in an hour, including schedule padding. Issue arise when, say, a destination is 28 minutes of schedule time from the pulse location. You can’t feasibly run it with one bus, since if that bus is at all delayed it will either delay other pulse buses or cause missed transfers. But putting two buses on the route is a poor use of resources, since each bus will now lay over more than half the time. So an hourly pulse network works only with routes where most round trips can be completed in under 50 minutes, and where others are long enough so that resources don’t sit idle. This is less of an issue with 30 minute pulses, as routes can be shorter and still align with the pulse.
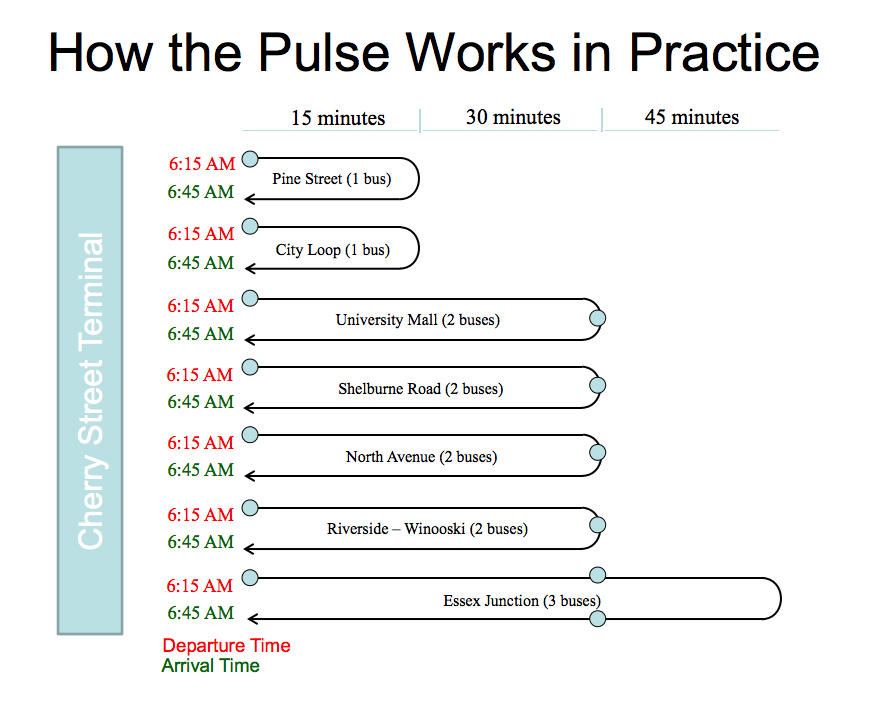 |
| Burlington, Vermont’s 30-minute pulse system shows how routes of different lengths operate with different numbers of buses; this is more difficult with an hour headway pulse. |
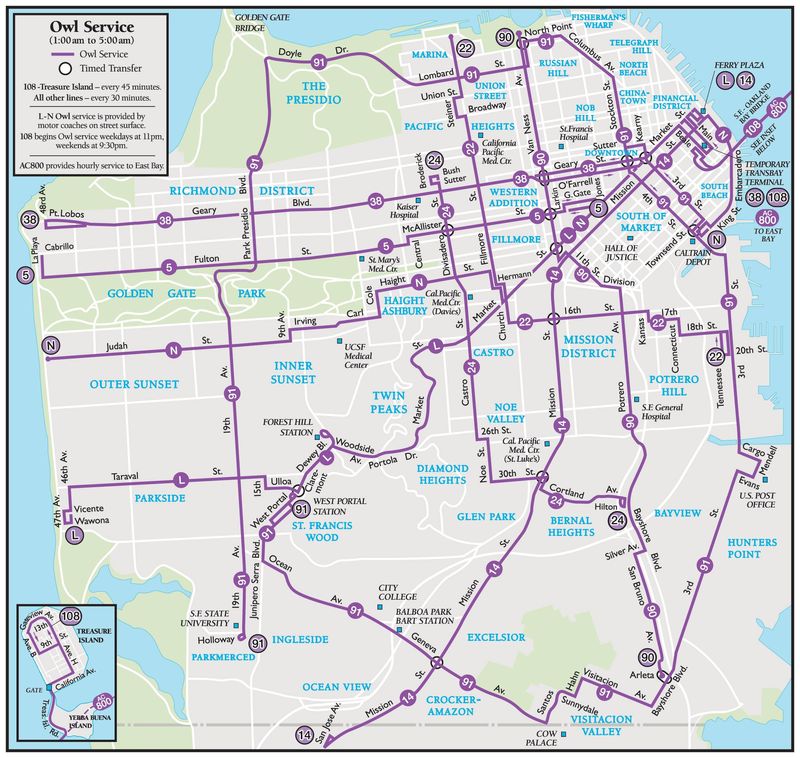 |
| San Francisco’s late night transit services involve a series of timed transfers. |