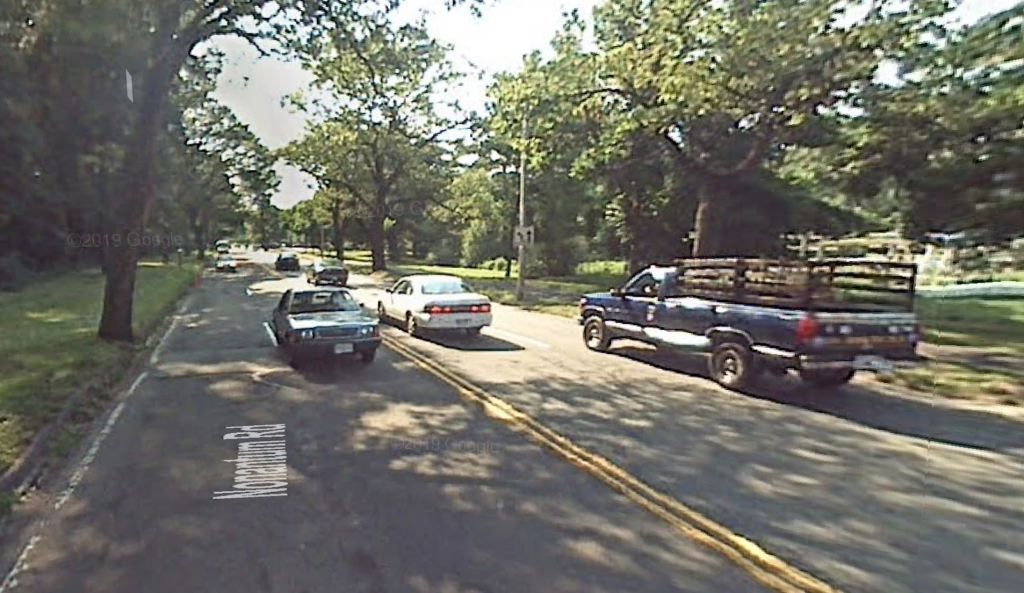
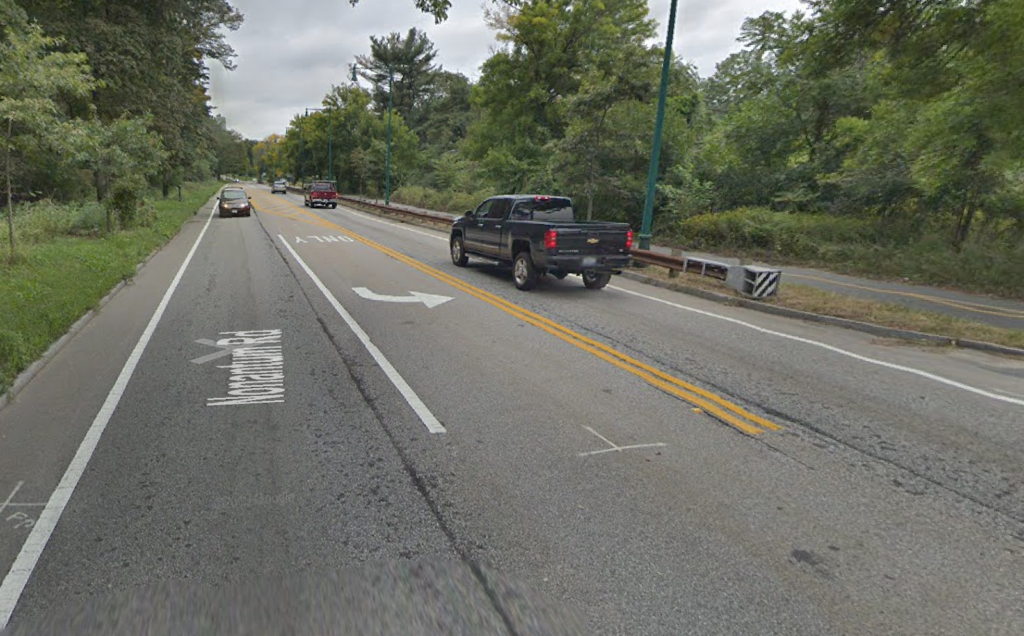
Memorial Drive in Cambridge—a pleasure roadway and a park—is actually a death trap. The wide, straight roadway encourages cars to speed, and speed they do, running over a pedestrian several times per year and killing people far too often. The roadway hosts no commercial vehicles, and the eastbound lanes serve only a couple of boating facilities between the BU and Longfellow bridges, yet the roadway—which was designed for low-speed horses and carriages—is built as if it were a highway, and any efforts to improve pedestrian safety have been stonewalled in the name of keeping traffic moving.
Except for a couple of traffic lights and poor-visibility sidewalks, traffic can proceed unimpeded from the BU Bridge to East Cambridge, on a straight, flat, mostly divided highway, where the 35 mph speed limit is honored in the breach. It’s no fun to walk across and only slightly more fun to walk or bike along. Officially, it’s a park, but it doesn’t seem like one.
Memorial Drive is part of the Charles River Basin park and there is a 2002 master plan for the basin. Portions of this plan have been implemented, including the new paths along the Cambridge side of the river, but the roadways have not been touched. (Believe it or not, until the 1990s, parking was allowed on both barrels of Memorial Drive, so there was even more pavement on Mem Drive east and a line of cars along the river.) The plan proposes narrowing the road slightly and moving the eastbound barrel inland from the river, slightly increasing the width of the park along the river. It says that other options were considered, but not advanced further in to the plan. One of these would have eliminated the eastbound roadway entirely, channeling all traffic on to the combined westbound barrel. Apparently removing the roadway would be incongruous with the historic nature of the roadway:
While there is some flexibility in applying
preservation criteria, the historic value of this cultural landscape would
be entirely lost under this alternative.
I call shenanigans. I don’t remember Frederick Law Olmsted planning for two lanes of 40 miles per hour automobile traffic in each direction, and parking. I think the DCR is afraid of reducing the number of lanes on the roadway. Rather than focusing on what the road looks like today, what if the DCR prioritized what would best serve as parkland for the public?
Instead of trying to rebuild the highway-like park (or is it a park-like highway) let’s consider moving traffic to the westbound lanes. Use this roadway for two lanes of traffic, turning lanes at intersections, pedestrian refuges between the lanes to minimize crossing distances and some parking where needed (and charge for it if you can’t figure out how to pay for the roadway changes). At the same and the eastbound lanes can be converted to parkland, increasing green space and allowing us to reclaim the dead space in between the current roadway. It might not match his parkway, but it would create a Cambridge esplanade. I think old Frederick Law would be proud.
There is an 80-foot-wide median between the two barrels of Memorial Drive today, but this is lost parkland, since it is nearly impossible to access and cut off from both MIT and the river, and who really wants to sit in a park in the middle of a highway anyway? If the roadway were consolidated, it the amount of useful parkland would go from 40 feet wide to 145 feet wide. On the MIT side, the portion of the parkland between the road and the sidewalk isn’t even grass, but instead wood chips and mud, since it receives heavy pedestrian use, so the road could actually be pushed north there. This would provide enough room for one lane of traffic in each direction, left turn bays on and off of Memorial Drive where needed, and parking spaces elsewhere. By using part of this space, no trees would be impacted (which would be the case of the roadway were moved south).
These two roadway designs carry the same number of vehicles.